Sulfuric acid production is a critical process in many industrial applications, but like any complex chemical manufacturing process, it can encounter various issues that impact efficiency and product quality. In this article, we’ll explore some of the common problems in the converter system of sulfuric acid plants and provide actionable solutions to keep the process running smoothly.
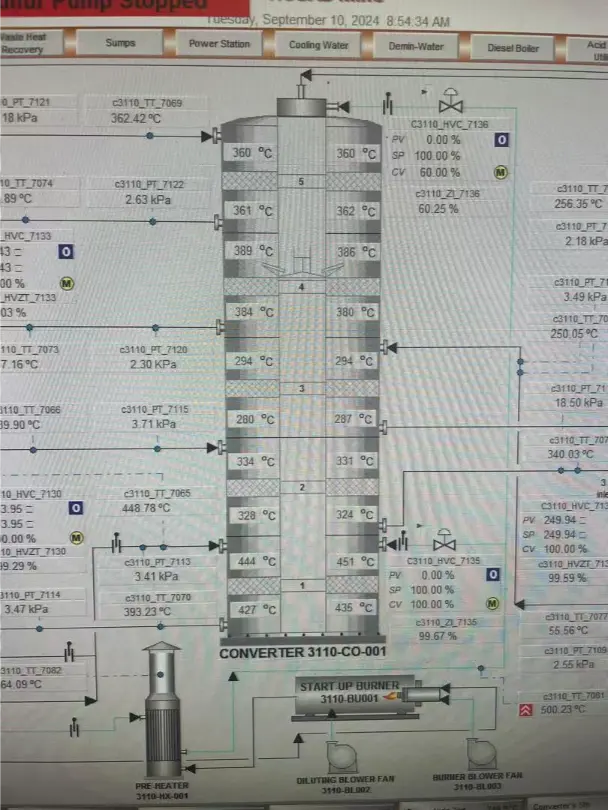
1. Low Heat-up Rate in the Converter
One of the most common issues in sulfuric acid production is a low heat-up rate during the preheating of the converter. This can be caused by insufficient dry airflow or improper temperature control of the preheated air.
Solution:
To solve this, it’s essential to increase the dry airflow and adjust the temperature of the preheated air to ensure the converter reaches the required operating temperature efficiently.
2. Temperature Drop After Sulfur feeding in Pass# 1 of the Converter
Another challenge is the drop in temperature in Pass# 1 of the Converter after sulfur feeding. This issue occurs because the blower takes too long to warm up, and the incoming gases are often too cold to reach the catalyst ignition temperature.
Solution:
To mitigate this problem, ensure the blower is activated and reaches full speed quickly, and make sure the incoming gases are heated to the required temperature before sulfur feeding.
3. Temperature Decrease Pass# 2 of the Converter After Sulfur Feeding
After catalytic reaction or SO2 oxidation in Pass# 1 of the converter, the gases undergo cooling in heat exchangers before entering Pass# 2. If the Pass# 1 outlet temperature is too low, the gases entering the second stage may not meet the necessary catalyst ignition temperature.
Solution:
Adjust the outlet temperature of Pass# 1 and fine-tune the bypass valve settings to ensure the temperature entering Pass# 2 is adequate for catalytic reactions to occur.
4. Shift in Conversion Load to Later Passes
When Pass# 1 temperatures are too low, the conversion rate decreases, causing a portion of the sulfur dioxide (SO2) that should have reacted in Pass# 1 to pass into the subsequent passes. This leads to an overload in the later passes of the converter.
Solution:
Regularly monitor and adjust the temperatures of each conversion pass, particularly the first pass, to maintain optimal conversion rates. If necessary, replace aging catalysts to improve efficiency and reduce the burden on downstream passes.
5. Excessive SO2 Concentration in the Off-gas Stack
Excess SO2 concentration in the off-gas stack is often caused by low conversion rates, catalyst degradation, improper gas concentration adjustments, and incorrect temperature control.
Solution: To address this, inspect the catalysts regularly and replace or screen them as needed. Adjust gas concentrations and operating conditions to optimize conversion rates and prevent SO2 from exceeding acceptable levels.
6. High Pressure Drop
High pressure drop in the conversion process can be caused by closed or partially opened valves, scaling in heat exchangers, or catalyst deactivation due to dust and other contaminants.
Solution:
Ensure all valves are fully open, and perform routine maintenance on heat exchangers and other components to prevent scaling. Screen the catalyst regularly to address issues such as rust or dust accumulation on the catalyst surface.
7. Gas Leaks from Equipment Shells
Gas leaks from the converter system equipment can occur due to corrosion, thermal expansion, or structural defects in the design or installation of the system. These leaks can negatively impact process efficiency and safety.
Solution:
Regularly inspect equipment for potential leaks and perform repairs as necessary. It’s also important to maintain a steady and gradual startup process to avoid temperature shocks that could exacerbate leaks. Properly maintain equipment to prevent corrosion and structural weaknesses.
Conclusion
Sulfuric acid production involves a complex system where temperature control, catalyst performance, and proper equipment maintenance play crucial roles in ensuring efficiency. By addressing common issues such as low heating rates, temperature fluctuations, and catalyst degradation, you can optimize your sulfuric acid production process, improve output quality, and reduce downtime. Regular maintenance, careful monitoring, and timely adjustments to the system are key to resolving these challenges and maintaining smooth operations.
By applying the solutions outlined above, sulfuric acid plants can avoid costly downtimes and improve the overall efficiency of their production processes, contributing to better resource utilization and more sustainable industrial practices.
For more information, continue reading our blogs!
You may be interested in Converters Maintenance (sulphuric-acid.com)





